Flag of Antigua and Barbuda
 | |
| Use | National flag and civil ensign |
|---|---|
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Adopted | February 27, 1967 |
| Design | A horizontal tri-colour of black, blue (half-width), and white, with two red right scalene triangles on opposite sides. On the black band is a yellow half-sun with nine rays |
| Designed by | Sir Reginald Samuel |
 | |
| Use | State ensign |
| Proportion | 2:3 |
| Design | A white field with a red cross, the national flag in the canton |

The national flag of Antigua and Barbuda was adopted on 27 February 1967 to mark the achievement of self-government. A competition to design the flag was held in which more than 600 local people entered. The winning design was put forth by nationally well-known artist and sculptor Sir Reginald Samuel.[1]
Design and symbolism
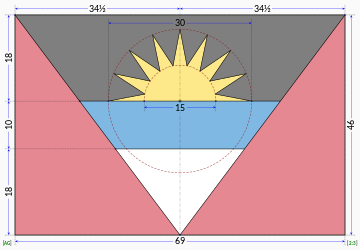
[edit]The design is a red field with an inverted isosceles triangle based on the top edge of the field pointed toward the bottom edge of the field bearing the horizontal tricolour of black, light blue (half width) and white with the rising sun centred on top of the black band. The rising sun symbolises the dawning of a new era.[2]
The colours have different meanings: the black is for the African ancestry of the people; the blue for hope; and the red for energy or life of the people. The successive colouring of black, yellow, blue, and white (from the sun down) also stands for the soil, sun, sea, and sand.[1] The blue also represents the Caribbean Sea, and the V-shape is the symbol of victory.[2] The seven points on the flag represent each of the six parishes and the island of Barbuda.[3]
The state ensign, which is used only by the national coast guard, consists of a white field, a red cross, and the state flag in the canton.
Construction Sheet
[edit]History
[edit]Pre-1967
[edit]From the beginning of European settlement on the islands in the 1630s, the flags of England (pre 1707), Great Britain (1707–1800), United Kingdom (1801–1871), British Leeward Islands (1871–1958) and West Indies Federation (1958–1962) were used over the islands. The first flag representing the territory of the present-day nation was created in the late 1950s, at which time Antigua and Barbuda were reorganized into a province of the West Indies Federation. This flag consists of a Blue Ensign defaced with the coat of arms. The coat of arms depicted the landscape of the island with an aloe-plant on the shore and a sugar mill on a hill. It is not known exactly when the coat of arms was developed, however, since 1909 this design has been used to represent Atigua on the larger coat of arms of the British Leeward Islands.[4] The Blue Ensign defaced with the local coat of arms is the common design on colonial flags throughout the British Empire, adopted by all the other provinces of the West Indies Federation. The original flag design included a white circle behind the coat of arms, but this element disappeared over time. For civilian use, especially on ships, there was a flag based on the Red Ensign.[5]
History of the current flag
[edit]The flag based on the Blue Ensign was replaced by the current design on 27 February 1967. This was 11 days after the Royal assent to the West Indies Act 1967, which changed the status of the islands from British colonies to states in free association with the United Kingdom. The flag adopted at that time was the design of Sir Reginald Samuel, which had won a public competition. Apparently it was one of the last projects admitted to the competition. After gaining full independence on November 1, 1981, the flag was retained.[6]
Other flags
[edit]Viceregal flags
[edit]| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
1967–1981 | Flag of the governor | |
 |
1981-2023 | Flag of the governor-general | |
 |
2023-present | Flag of the governor-general |
Barbuda
[edit]| Flag | Date | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
1997-2018 | Flag of the Barbuda Council | |
 |
2018-present | Flag of the Barbuda Council | Barbuda Flag of Self-Determination[7] |
References
[edit]- ^ a b "flag of Antigua and Barbuda | Britannica". www.britannica.com. Retrieved 2022-08-19.
- ^ a b "CIA World Factbook- Antigua and Barbuda". Retrieved 8 July 2019.
- ^ "Antigua & Barbuda: Antigua and Barbuda Flag". www.antiguanice.com. Retrieved 2022-02-26.
- ^ de Vries, Hubert. "ANTIGUA". hubert herald. Retrieved 2010-02-14.
- ^ "Antigua and Barbuda - Colonial Flags (1956-1967)". crwflag. Retrieved 2021-08-25.
- ^ "Antigua & Barbuda: Antigua and Barbuda Flag". www.antiguanice.com. Retrieved 2022-02-26.
- ^ "PlanBarbuda - THE FLAG". www.planbarbuda.org. Retrieved 2024-03-07.
External links
[edit]- Antigua and Barbuda at Flags of the World
- Antigua and Barbuda - Colonial Flags (1956-1967) at Flags of the World